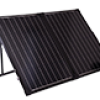
PRODUCT CATEGORY

Main title
Sub title

Main title
Sub title

Main title
Sub title
Latest Products

Since 2010 we have been on a mission to change the way the world uses energy. We are committed to making a lasting impact on planet earth by removing barriers to sustainable living and energy independence.
Our mission is to empower the energy independence of 50 million people with DIY-friendly and reliable renewable energy products by the year 2030.